 With Clip Export, a section of a map window can be exported to various CAD and GIS output formats. Only the objects within the desired section are exported (clipping). The export can span several levels at the same time.
With Clip Export, a section of a map window can be exported to various CAD and GIS output formats. Only the objects within the desired section are exported (clipping). The export can span several levels at the same time.
Set clipping area
a)Activate the tool button and draw a clipping area (rectangle) in a map window that contains all the objects to be exported.
b)Select any region object that should serve as the boundary for the clipping area and then activate the tool button.
Settings and Options
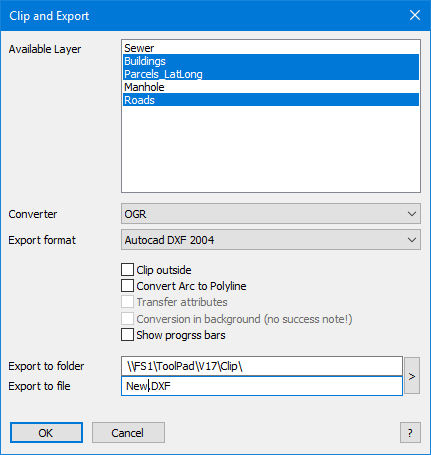
Available Layer
The export dialog displays all exportable layers contained in the map window (without cosmetic layer, seamless layer and raster layer). Select all layers to be exported (hold down the Ctrl key for multiple selection).
Converter and Export formats
MapInfo |
OGR |
Universal Translator (UT) |
MapInfo TAB |
AutoCAD DXF |
AutoCAD DXF |
MapInfo WOR + TAB |
ESRI Shape SHP |
AutoCAD DWG |
MapInfo MIF / MID |
GML Version 2 |
ESRI SHP |
|
GML Version 3 |
ESRI GDB File Geodatabase |
|
|
Microstation DGN |
OGR is based on the GDAL / OGR Simple Features Library C ++ library. Universal Translator is included in the default installation of MapInfo Pro.
Options
Cut outside |
all convertrer |
Cuts surface and line objects outside the clipping area. |
Convert Arc to Polyline |
all convertrer |
Arcs are converted to polylines when converted. This may be required if the target program's import routine does not support arcs. Note: The OGR converter always converts arcs into polylines. |
Transfer attributes |
Universal Translater |
Database contents are written as attributes in the DXF / DWG file. By taking over the attribute data, the output file can become very large and many programs can not evaluate the attribute data. |
Conversion in background |
Universal Translater |
The export is started as a separate process (recommended for large amounts of data). MapInfo can still be used. The result is not checked and the temporary files are not deleted. |
Show progress bars |
all convertrer |
In order to receive feedback on the status of the export for large amounts of data, the option Show progress bars can be activated. |
Output directory / Output file
Format |
Typ |
DWG, DXF, DGN |
File. A single file with separate layers. The layer names in the file correspond to the original table names. |
SHP |
Directory. Separate files for each layer. If different geometry types exist in a table, they are stored in different shape files |
GDB |
File and directory. Although a file with the extension * .gdb must be specified in the dialog, the converter automatically generates a directory from it. This is unusual, but the ESRI geodatabase uses such a directory with extension; the directory name ends with.gdb. |
TAB, MIF |
Directory. Separate files for each layer. The target layer name is preceded by a sequential number. (Example: Location => T3_location.tab). |
TAB + WOR |
File. The workspace (WOR) is saved under the specified name. For each layer, a native table is created in the same directory. The destination file name is preceded by a sequential number. (Example: Location => T3_location.tab). |
GML |
Directory. Separate files for each layer. In addition to the GML file, a schema file (XSD - XML Schema Definition) is created for each layer. |
 Hints
Hints
•If a rectangle has been raised and there is a selection in parallel, a corresponding note appears.
•If the tables are in different projections, you may need to select a single target projection (only OGR and UT).
•MapInfo collections and multipoints are preserved only if the target format is MapInfo again. For Universal Translator and OGR, these objects are automatically split into individual objects.
•Saving directly to a root directory is not possible (for example, E: \).
•When exporting to the ESRI shape format, note the following:
•For reasons of compatibility, umlauts are converted to layer names. Layer names should not be longer than 20 characters.
•The shape format saves the data in * .dbf format. DBase has a limit of 10 characters for the column name. Longer field names are therefore shortened during export.
•The shape format stores geometries only "sorted". If different geometry types were stored within a relation, a separate * .shp is generated for each geometry type.
•The target layer name is preceded by a sequential number and the object type is appended. (Example: MyTable => T2_MyTable_polylinie.shp).